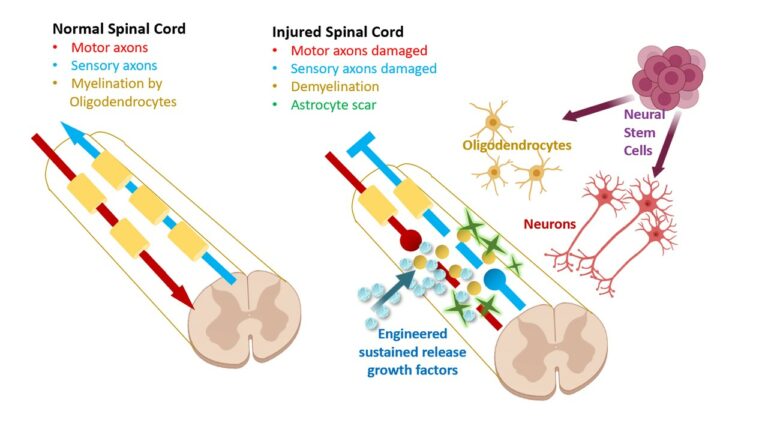
- If the nerve has been only partially compressed or severed, it can repair itself over time. ...
- Take non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAID) or acetaminophen. These medications should be used to treat acute pain sporadically or for no more than one to two weeks, unless recommended by a ...
- Try physical therapy. If a nerve was pinched, rather than severed, physical therapy (PT) is often used to repair the damage and increase strength and mobility.
- Sign up for acupuncture therapy. Some patients find that acupuncture calms the nerves and allows them to continue normal function while the nerves repair themselves.
Can neurons repair themselves even a little bit?
Can neurons repair themselves? Nerve Cells Do Not Renew Themselves Yet, nerve cells in your brain, also called neurons, do not renew themselves. They do not divide at all. There are very few exceptions to this rule – only two special places in the brain can give birth to new neurons. For the most part though, the brain cannot replenish dead ...
Can dead brain cells regenerate?
Until recent decades, doctors believed a certain level of brain degeneration is inevitable because your brain had a limited capacity to regenerate. Now we know better. New research from the last two decades suggests that your brain is actually able to create new cells throughout your lifespan and brain regeneration is possible.
Can the brain regrow itself?
For almost 100 years, it had been a mantra of biology that brain cells or neurons do not regenerate. It was thought that all your significant brain development happened from conception to age 3. Contrary to that widely held popular belief, scientists now know that neurogenesis continuously occurs in specific regions in the adult brain.
Why don't brain cells regenerate?
The brain actually can’t regenerate itself well because when the brain is damaged its cells find it harder to make new ones. This is because the brain has very few of the special cells, or stem cells. In recent years, we’ve found some areas of the brain can regenerate.

Can damaged neurons regrow or heal?
Neurons in the brain and spinal cord don't grow back after injury, unlike those in the rest of the body. Cut your finger, and you'll probably be back to using it in days or weeks; slice through your spinal cord, and you likely will never walk again.
What helps damaged neurons regenerate?
This is because these neurons have a different lining, or sheath, made up of Schwann cells. The central nervous system does not have these cells. Schwann cells can help damaged nerves regenerate and restore function.
What can repair neurons?
There is something known as a “stem cell” that seems to be a promising option to regenerate damaged neurons in the brain. Stem cells are a special type of cells that can be trained to develop into any kind of cell, such as a neuron.
What happens if your neurons are damaged?
Neurons are fragile and can be damaged by pressure, stretching, or cutting. An injury to a neuron can stop the signals transmitted to and from the brain, causing muscles to not work properly or a loss of feeling in an injured area. Nerve injuries can impact the brain, the spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
Can neurons be repaired?
Most of your neurons can't be replaced. Other parts of your body -- such as skin and bone -- can be replaced by the body growing new cells, but when you injure your neurons, you can't just grow new ones; instead, the existing cells have to repair themselves.
Can neurons regrow?
Yet, nerve cells in your brain, also called neurons, do not renew themselves. They do not divide at all. There are very few exceptions to this rule – only two special places in the brain can give birth to new neurons. For the most part though, the brain cannot replenish dead neurons.
Can neuron damage be reversed?
While damage to the brain cannot be reversed, functions affected by TBI can be recovered thanks to the brain's natural ability to rewire itself. To help you better understand recovery after traumatic brain injury, this article will discuss: Is traumatic brain injury permanent?
How can I improve my neurons?
New neurons enhance your ability to learn. Growing new neurons can help you stave off Alzheimer's....How to Grow New Brain CellsEat Blueberries. ... Indulge in Dark Chocolate. ... Keep Yourself Engaged. ... Eat Omega-3 Fatty Acids. ... Exercise. ... Eat Turmeric. ... Have Sex. ... Drink Green Tea.More items...
How long does it take to regrow neurons?
The brain can make thousands of new neurons every day and maintains this ability well into old age. By the time you turn 50, you will have replaced the original neurons in your hippocampus, your brain's “memory center,” with all new neurons!
How do neurons regenerate?
In addition to building fitness, regular endurance exercises like running, swimming, or biking can preserve existing brain cells. They can also encourage new brain cell growth. Not only is exercise good for your body, it can also help improve memory, increase focus, and sharpen your mind.
How do you regenerate nerves naturally?
Green and leafy vegetables. Broccoli, spinach and asparagus all contain vitamin B, a nutrient important for nerve regeneration and nerve function. Spinach, broccoli and kale also contain a micronutrient called alpha-lipoic acid that prevents nerve damage and improves nerve function.
What type of treatment can be used to help regenerate neurons?
Researchers in the Center for Regenerative Medicine hypothesized that mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) can rescue damaged neurons after exposure to oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) stress. Studies have demonstrated that the MSC can differentiate into bone, cartilage and fat tissues.
How do neurons regenerate?
In addition to building fitness, regular endurance exercises like running, swimming, or biking can preserve existing brain cells. They can also encourage new brain cell growth. Not only is exercise good for your body, it can also help improve memory, increase focus, and sharpen your mind.
How can we increase neurons in brain?
Aerobic activities such as running, cycling, swimming, and even sex, are effective ways of boosting neurogenesis. The aim is getting the heart pumping for more than 20 minutes at a time, and on a regular basis. In this state levels of several growth hormones are elevated in the brain.
Can the damaged brain repair itself?
And the answer is yes. The brain is incredibly resilient and possesses the ability to repair itself through the process of neuroplasticity. This phenomenon is the reason why many brain injury survivors can make astounding recoveries.
What was the purpose of the team's genetically removed syntaphilin?
This allowed mitochondria to regain mobility and resulted in the regrowth of other mitochondria that eventually restored the neurons’ ability to repair themselves.
What is the protein that controls mitochondrial movement?
Mitochondria are mobile in young cells and as a cell matures, the movement is restricted by a protein called syntaphilin. This protein behaves as a brake or anchor for mitochondria.
Is nerve cell regeneration possible?
Scientists have found out that nerve cell regeneration is possible. Researchers from National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke in the US restored mitochondrial mobility in a group of mice and observed regeneration of nerve cells.
What is the role of the choroid plexus in neuronal repair?
Following brain or spinal cord ischemia, there is compensatory upregulation and distribution of many growth factors that contribute significantly to neuronal repair. Working homeostatically in concert with glial and cerebral endothelial cells, the epithelium of the choroid plexus secretes numerous peptides and proteins into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which conveys these trophic factors, by volume transmission, to neurons at damage sites. Forebrain injury by transient global or focal ischemia results in considerable morbidity to choroid epithelial cells at the blood-CSF barrier; however, despite marked ischemic damage to the choroidal parenchyma, restorative processes ensure that the structural and functional integrity of this key transport interface is regained within several hours of interrupted blood flow. There is also an injury-induced elevation of growth factors in CSF and tissues bordering the cerebroventricular system. Our working hypothesis for the forebrain injury model is that the lateral choroid plexus-ventricular CSF system has an integral role in minimizing damage to adjacent regions, such as the hippocampus, by acting as a source in supplying trophic factors and as a sink in removing potentially deleterious metabolites. We marshal evidence that CSF-administered growth factors, delivered pre- as well as postischemia, attenuate neuronal damage or promote repair of injured brain and cord. Thus the choroid plexus, an expression source of numerous growth factors, is a useful protein- and CSF-generating organ for boosting growth factor availability to stressed neuropil regions.
What is neurogenesis in MDD?
Neurogenesis is a dynamic and continual process occurring upon environmental stimuli, and is characterized by the differentiation and survival of neural progenitor cells into newly born neurons ( Haughey et al., 2002; Kim et al., 2008 ). These newborn neurons form synapses with preexisting neurons and extend the functional connectivity of the neuronal networks ( Taupin, 2006 ). Stress is a precipitant factor of MDD down-regulates hippocampal neurogenesis ( Sen et al., 2008) and results in subsequent hippocampal mal-adaptive changes and atrophy ( Campbell et al., 2004; Malberg et al., 2000; Watanabe et al., 1992 ). Interestingly, a reduction in hippocampal size has been reported both in stressed animals ( Watanabe et al., 1992) as well as in the brain of depressed patients ( Campbell et al., 2004; MacMaster and Kusumakar, 2004 ). In contrast, antidepressant regimens avert this effect possibly through inducing neurotrophic expression and subsequent neurogenesis ( Karege et al., 2002; Malberg et al., 2000; Sen et al., 2008; Taliaz et al., 2010 ). Clinical findings have shown lower levels of GDNF ( Diniz et al., 2013 ), NGF ( Wiener et al., 2015 ), as well as BDNF ( Karege et al., 2002) in MDD patients than healthy subjects. Beside this, a reduced amount of neurotrophic factors may be linked to symptoms such as locomotor slowing, agitation, and anxiety observed in patients with MDD ( Karege et al., 2002 ). Notably, preclinical studies with rodents have shown that infusion of BDNF into the cerebral structures including midbrain, hippocampus, or lateral ventricles induce antidepressant effects ( Duman and Monteggia, 2006; Sen et al., 2008 ). Naumenko et al. (2014) have demonstrated that intracerebral delivery of NGF improved spatial memory impairment in antidepressant sensitive cataleptics mice; however, it did not produce an antidepressant effect. These findings suggest a role for NGF and BDNF in the regulation of brain plastic changes to overcome environmental stimuli ( Berry et al., 2012 ).
What are neurotrophic factors?
Neurotrophic factors are a group of small proteins that mediate survival, maturation, and differentiation of neurons by binding to specific kinase receptors. They regulate neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity, and neuronal repair, as well as maintenance of neuronal connectivity (Nasrolahi et al., 2018 ).
Can CNTs be used for stroke prevention?
This idea stems from the fact that CNTs proved effective in providing a matrix for neuronal repair in vitro due to their electrical properties (Hernandez-Ferrer et al., 2014; Kam et al., 2009; Mattson et al., 2000 ), and could therefore be used as scaffolding for stem cell therapy. The preliminary observations by Lee et al. showed that SWNTs scaffolding, even without using stem cells, reduced the size of the infarcted brain areas following ischemic injury suggesting a neuroprotective role in the brain ( Lee et al., 2011 ).
Does VEGF cause brain edema?
Taking together, the effects of VEGF on brain edema formation are still controversial. VEGF has most probably very early detrimental effects on vascular permeability and the BBB, but beneficial effects on early and late angiogenesis, revascularization, perilesional microcirculation, and neuronal repair may outweigh its detrimental effects.
How do neural stem cells help with spinal cord injury?
In recent years, researchers have significantly advanced the possibility of using grafted neural stem cells to spur spinal cord injury repairs and restore lost function, essentially by inducing neurons to extend axons through and across an injury site, reconnecting severed nerves.
What happens to the brain when it is injured?
When adult brain cells are injured, they revert to an embryonic state , say researchers. In their newly adopted immature state, the cells become capable of re-growing new connections that, under the right conditions, can help to restore lost function.
When brain cells are injured, they revert to an embryonic state?
When adult brain cells are injured, they revert to an embryonic state, according to new findings published in the April 15, 2020 issue of Nature by researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, with colleagues elsewhere. The scientists report that in their newly adopted immature state, the cells become capable ...
Where are new brain cells produced?
But work by Fred "Rusty" Gage, PhD, president and a professor at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies and an adjunct professor at UC San Diego, and others found that new brain cells are continually produced in the hippocampus and subventricular zone, replenishing these brain regions throughout life.
Can immature cells restore function?
The scientists report that in their newly adopted immature state, the cells become capable of re-growing new connections that, under the right conditions, can help to restore lost function. advertisement. Repairing damage to the brain and spinal cord may be medical science's most daunting challenge.
Is it possible to repair the brain?
Repairing damage to the brain and spinal cord may be medical science's most daunting challenge. Until relatively recently, it seemed an impossible task. The new study lays out a "transcriptional roadmap of regeneration in the adult brain."
How do neural stem cells help with spinal cord injury?
In recent years, researchers have significantly advanced the possibility of using grafted neural stem cells to spur spinal cord injury repairs and restore lost function, essentially by inducing neurons to extend axons through and across an injury site, reconnecting severed nerves.
What happens to the brain after injury?
Using a mouse model, Tuszynski and colleagues discovered that after injury, mature neurons in adult brains revert back to an embryonic state. “Who would have thought,” said Tuszynski. “Only 20 years ago, we were thinking of the adult brain as static, terminally differentiated, fully established and immutable.”.
Where are new brain cells produced?
But work by Fred “Rusty” Gage, PhD, president and a professor at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies and an adjunct professor at UC San Diego, and others found that new brain cells are continually produced in the hippocampus and subventricular zone, replenishing these brain regions throughout life.
When do brain cells revert to embryonic state?
April 15 , 2020 | Scott LaFee. News_release. When adult brain cells are injured, they revert to an embryonic state, according to new findings published in the April 15, 2020 issue of Nature by researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, with colleagues elsewhere. The scientists report that in their newly adopted immature ...
Is it possible to repair the brain?
Repairing damage to the brain and spinal cord may be medical science’s most daunting challenge. Until relatively recently, it seemed an impossible task. The new study lays out a “transcriptional roadmap of regeneration in the adult brain.”
How to transform addictive biochemistry back to healthy neurochemistry?
Allowing adequate time for new habits to form, providing adequate education to make better life and health choices, neurotoxin removal, and following nutritional guidance to restore healthy levels needed can all work together to transform addictive biochemistry back to healthy neurochemistry.
How to improve cognitive deficits?
Exercise – Staying active is beneficial in recovery and can improve cognitive deficits that often accompany addiction, drug dependence, and in the various phases of recovery. Exercise invites rebalancing neurochemistry in a natural way. 15,28
What is the role of noradrenaline in the brain?
Noradrenaline – also called norepinephrine, is a stimulating neurochemical that supports alertness, learning, perception, and other cognitive functions. When you watch an exciting movie, or when you perform on stage, or you become alert to some threat, a surge of noradrenaline (and its close relative, adrenaline) flows. When noradrenaline is administered by injection, it can literally bring back the dead in the case of certain drug overdoses. 18,19 Too much noradrenaline can cause panic, overstimulation, and even cardiac arrest. 20 A bit like having money in the bank, noradrenaline is vital to overcoming stressful situations and can be supported with a healthy diet and other factors, which will be detailed below.
What is the role of gamma-amino butyric acid in the nervous system?
Gamma-amino butyric acid aka GABA – GABA is the neurotransmitter responsible for calming the nervous system. GABA deficiency is linked to panic attacks, stress, and the inability to calm down, rapid or uneven heartbeat, muscle tension, difficulty breathing, sweaty palms, and even the inability to understand or explain emotions that you are feeling. An overabundance of GABA can result in excessive, unrefreshing sleep and stroke. Benzodiazepines can become addictive due to their GABA-ergic effects. 17 Diet and supplements are effective ways to efficiently re-balance GABA levels.
How do drugs affect the brain?
Your brain is naturally always changing. Introducing drugs to your system can influence these changes to be more dramatic and even life-threatening. Dopaminergic drugs such as cocaine highjack the neurons in the reward sector of your brain. This makes you feel good when you take the drug because it has now become the agent that releases more dopamine instead of the things in life that used to do that, such as hugging a friend or perhaps listening to music. The drug artificially provides an intense rush of good feelings. This change or “high” will only last a short time, but the actual change in your brain chemistry will last much longer. Your ability to handle cravings will become increasingly more difficult, and cravings will become more serious and demanding. Drugs impact the brain on many different levels, and the neurotransmitter affected may differ depending on the drug of choice.
Does MDMA affect the brain?
It most typically alters the ability of neurons to transmit serotonin, which is vital to many functions of the brain. Long-term use of ecstasy commonly results in deep depression, due to this neurochemical damage. 24
Does marijuana harm the brain?
Heroin/Prescription Opioids/Marijuana – These drugs mimic various natural brain chemicals and bind to their receptor sites instead of the body’s own chemicals. This interference disrupts the natural transmission and shuts down the normal production of neurotransmitters. Repeated or chronic abuse can lead to the brain becoming rewired as it struggles to try and maintain balance.
How do damaged neurons affect mental health?
Damaged neurons can negatively impact our mental health and lead to emotional problems like apathy or personality disorders. Sometimes, these problems can be remedied by restoring function to the damaged areas of the brain by promoting neurogenesis.
How many neurons do we regenerate in our brain?
We now know this isn’t true - the human brain has been shown to regenerate at least 700 neurons a day in the hippocampus alone.
What Can Neurogenesis Do?
As you can imagine, neurogenesis has remarkable potential. The fact that our brains can grow new cells suggests that we can repair cognitive damage that has been done through months or years of abuse.
How does new knowledge help the brain?
New knowledge strengthens the network of connections between neurons and makes it easier for them to communicate, stimulating growth and making it easier to use the brain cells that are already functioning.
How many neurons does the brain have?
The 700 neurons our brain creates in a day might not seem like much, and relatively speaking, it’s not. However, there are some things that you can do to speed up your brain’s ability to produce new brain cells.
What is the function of neurogenesis?
Neurogenesis is a vital function for our mental health and it helps us retain our cognitive ability as we grow older .
How does learning help the brain?
By learning something new, you force your brain to create new neural connections, and overtime the continual learning process strengthens the network between new information and things you already know.