Procedures
What increases my risk for heart block?
- Past heart attack or heart failure
- Heart valve conditions or surgery on your heart valves
- Some medicines, or being exposed to toxins
- Lyme disease
- Older age
Nutrition
Thallium Stress Test (MPI or MUGA)
- Helps measure blood flow of your heart muscle at rest and during stress.
- Helps determine extent of a coronary artery blockage.
- Helps determine extent of damage from heart attack.
- Helps determine cause of chest pain ( angina ).
- Helps determine level of safe exercise for patients.
What medications cause complete heart block?
by jcb - 2020-10-13 10:06:19. Guidelines say: Permanent pacemaker implantation is indicated for advanced second- or third-degree AV block associated with symptomatic bradycardia, ventricu-. lar dysfunction, or low cardiac output. (Level of Evidence: C)
What medical tests show heart blockage?
You treatment depends on the type of heart block you have:
- With first-degree heart block, you might not need treatment.
- With second-degree heart block, you may need a pacemaker if symptoms are present or if Mobitz II heart block is seen.
- With third-degree heart block, you will most likely need a pacemaker.
When is a pacemaker needed for heart block?
What is treatment for complete heart block?
Can heart blockage be cured?
Unfortunately, there isn't a cure for coronary artery disease, and you can't reverse this condition once you're diagnosed. But you can make lifestyle changes to reduce your risk of developing further health problems, such as a heart attack.
How do you clear a heart blockage?
A small tube called a stent, which may contain medication, can be placed in an artery to maintain adequate blood flow. A catheter is used through the artery of the leg to reach the heart, and a stent is put in place through the catheter in the area of the blockage. Bypass surgery.
Can heart blockage be cleared naturally?
Though there is little you can do to unclog arteries, you can do a lot to prevent additional buildup. A heart-healthy lifestyle can help you lower your levels of artery-clogging LDL cholesterol. It can also help you be healthier overall.
Can you reverse blocked arteries?
Medical treatment, regular exercise, and dietary changes can be used to keep atherosclerosis from getting worse and stabilize the plaque, but they aren't able to reverse the disease.
What are the early signs of heart blockage?
SymptomsChest pain, chest tightness, chest pressure and chest discomfort (angina)Shortness of breath.Pain, numbness, weakness or coldness in your legs or arms if the blood vessels in those parts of your body are narrowed.Pain in the neck, jaw, throat, upper abdomen or back.
How much blockage is normal?
A moderate amount of heart blockage is typically that in the 40-70% range, as seen in the diagram above where there is a 50% blockage at the beginning of the right coronary artery. Usually, heart blockage in the moderate range does not cause significant limitation to blood flow and so does not cause symptoms.
How do you clear a blocked heart without surgery?
Through angioplasty, our cardiologists are able to treat patients with blocked or clogged coronary arteries quickly without surgery. During the procedure, a cardiologist threads a balloon-tipped catheter to the site of the narrowed or blocked artery and then inflates the balloon to open the vessel.
What does a heart blockage feel like?
A completely blocked coronary artery will cause a heart attack. The classic signs and symptoms of a heart attack include crushing chest pain or pressure, shoulder or arm pain, shortness of breath, and sweating. Women may have less typical symptoms, such as neck or jaw pain, nausea and fatigue.
Can you live with heart blockage?
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is treatable, but there is no cure. This means that once diagnosed with CAD, you have to learn to live with it for the rest of your life. By lowering your risk factors and losing your fears, you can live a full life despite CAD.
At what age do arteries start clogging?
By the age of 40, about half of us have cholesterol deposits in our arteries, Sorrentino says. After 45, men may have a lot of plaque buildup. Signs of atherosclerosis in women are likely to appear after age 55.
What dissolves artery plaque?
There are no quick fixes for melting away plaque, but people can make key lifestyle changes to stop more of it accumulating and to improve their heart health. In serious cases, medical procedures or surgery can help to remove blockages from within the arteries.
What foods unclog your arteries naturally?
Eat These 10 Foods to Cleanse Your ArteriesAsparagus. Asparagus is one of the best foods to cleanse your arteries. ... Avocado. Avocado helps reduce the “bad” cholesterol and increase the “good cholesterol” that helps to clear the arteries. ... Broccoli. ... Fatty Fish. ... Nuts. ... Olive Oil. ... Watermelon. ... Turmeric.More items...•
What does a heart blockage feel like?
A completely blocked coronary artery will cause a heart attack. The classic signs and symptoms of a heart attack include crushing chest pain or pressure, shoulder or arm pain, shortness of breath, and sweating. Women may have less typical symptoms, such as neck or jaw pain, nausea and fatigue.
Do all heart blockage require surgery?
Angioplasty may be done during your cardiac catheterization if your care provider thinks it's the best treatment option for you. If your arteries are narrowed or blocked in several areas, or if you have a blockage in one of the larger main arteries, coronary bypass surgery may be necessary.
Can you live with heart blockage?
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is treatable, but there is no cure. This means that once diagnosed with CAD, you have to learn to live with it for the rest of your life. By lowering your risk factors and losing your fears, you can live a full life despite CAD.
What percentage of artery blockage requires surgery?
If a carotid artery is narrowed from 50% to 69%, you may need more aggressive treatment, especially if you have symptoms. Surgery is usually advised for carotid narrowing of more than 70%. Surgical treatment decreases the risk for stroke after symptoms such as TIA or minor stroke.
How to keep your heart healthy?
Steps you can take to keep your heart and body as healthy as possible include: Lead a heart-healthy lifestyle, which includes eating a heart healthy diet, exercising regularly, getting an adequate amount of sleep each night, reducing stress, limiting alcohol and stopping smoking and use of illicit drugs.
What is the mildest heart block?
First-degree heart block: The electrical impulse still reaches the ventricles, but moves more slowly than normal through the AV node. The impulses are delayed. This is the mildest type of heart block. Second-degree heart block is classified into two categories: Type I and Type II.
What medications slow the heart's electrical impulses?
You take medications that slow the conduction of the heart’s electrical impulses including some heart medications (beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin), high blood pressure drugs, antiarrhythmics; muscle relaxants and sedatives; antidepressants and antipsychotics; diuretics; lithium.
What is the name of the block that makes your heart beat?
Heart Block. Heart block, also called AV block, is when the electrical signal that controls your heartbeat is partially or completely blocked. This makes your heart beat slowly or skip beats and your heart can’t pump blood effectively. Symptoms include dizziness, fainting, tiredness and shortness of breath. Pacemaker implantation is ...
How long do you need to wear a Holter monitor?
You may need to wear a portable ambulatory monitor device, such as a Holter monitor or an event recorder, for 24 to 48 hours or longer to collect more information about your heart’s electrical activity. If you need to use a monitor, you’ll get detailed information about how to use it.
Do you need a pacemaker for a heart block?
Second-degree block: If you have second-degree heart block and have symptoms, you may need a pacemaker to keep your heart beating like it should. A pacemaker is small device that sends electrical pulses impulses to your heart.
Can heart block cause lightheadedness?
Type of heart block, its location and severity, and symptoms vary from person to person. If left untreated, severe heart block can cause sudden cardiac arrest (your heart suddenly stops beating), but most commonly can cause either lightheadedness or fainting spells.
What is the best procedure for blockages?
At this stage, the best procedure for these types of blockages is coronary bypass surgery. Other associated risks: There is a less than 2% chance that a patient will suffer a heart attack or require emergency bypass surgery during coronary angioplasty.
What is the best treatment for calcified ridge blockages?
This is only beneficial in about 1 percent of cases. Rotational atherectomy: This uses a diamond-studded drill-bit to pulverize blockages. This is particularly useful for calcified, ridge blockages that are present in about 5 percent of cases. Lasers: These use tiny laser beams that can vaporize plaques.
Why are stents used in arteries?
The stent holds the narrowed artery open wider and reduces the likelihood that the artery will become narrowed again. Some stents are being designed with clot-busting medication, or with radiation, because studies have shown that both may be effective in preventing arteries from narrowing again.
How long does angioplasty pain last?
The discomfort in the chest, arm and leg lasts for 3-6 weeks. Requirement for subsequent procedures: About 20-25% of people who have angioplasty will need to have it repeated within a year, compared to less than 5% of coronary bypass patients who need to have a repeat bypass surgery within a year.
How long does it take to walk after bypass surgery?
The patient must lie flat for about six hours but can be up and walking soon and go home within the next 2-3 days. Bypass surgery traditionally involves splitting the breast bone. Most of the discomfort stems from this and from the incision in the arm or leg, from where the conduits (blood vessels) are taken.
What is the goal of a directional atherectomy?
The goal is to reduce complications, lower the frequency of re-blockage, and improve the success rate for less than ideal candidates. Other techniques that are occasionally used include: Directional atherectomy: This is done using a miniature rotating blade to cut out the fatty deposit and remove it from the body.
Can fatty deposits cause angina?
Depending on the degree of blockage, the patient may experience varying degrees of chest discomfort, called angina, during physical exertion. Even a heart attack may occur if blood flow in ...
How to tell if an artery is blocked?
Warning signs when an artery is blocked, and how to fix it. The symptoms of an artery blockage include chest pain and tightness, and shortness of breath. Imagine driving through a tunnel. On Monday, you encounter a pile of rubble. There is a narrow gap, big enough to drive through. On Tuesday, you're driving through the tunnel ...
What are the symptoms of a blocked artery?
The symptoms – chest pain, tightness and shortness of breath – can be similar, though. Sometimes, when arteries become completely blocked, a new blood supply develops around the blockage. This new blood supply, called collaterals, won't deliver as much blood to your heart. This can lead to those same symptoms of chest pain and shortness of breath . ...
What is a boulder in cardiology?
In cardiology, the boulder is called a Chronic Total Occlusion (CTO). It means the artery is completely blocked. This occurs in 15% to 20% of patients who have heart disease. Sometimes there has been a complete blockage for many months or even years. However, only about 3% to 5% of these patients undergo a stent or bypass procedure, ...
What are the tunnels in the heart?
Now translate those examples to your health. The tunnels are the arteries that carry blood to your heart. The rubble and boulders are blockages that can lead to problems – shown through symptoms. Blocked tunnels aren’t good for traffic flow, and blocked arteries aren’t good for your heart.
Can stress test cause shortness of breath?
This can lead to those same symptoms of chest pain and shortness of breath. If you have these symptoms, a stress test can help determine if they are caused by a blockage in an artery or something else. The first step is to see a doctor.
What is a moderate heart blockage?
A moderate amount of heart blockage is typically that in the 40-70% range, as seen in the diagram above where there is a 50% blockage at the beginning of the right coronary artery. Usually, heart blockage in the moderate range does not cause significant limitation to blood flow and so does not cause symptoms. Moderate coronary artery disease is treated much in the same way as mild disease, basically attention to risk factors, medications, and healthy lifestyle modification. Occasionally, heart blockage at the higher end of the moderate range (50-70%) may require additional testing to see if it is significant or not and may be responsible for symptoms.
What is 80% blockage?
Severe heart blockage is typically that in the greater than 70% range. This degree of narrowing is associated with significantly reduced blood flow to the heart muscle and can underlie symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath. In the diagram above, an 80% blockage can be seen at the beginning of the vessel. This is actually a bypass graft in someone that has had bypass surgery. The severe heart blockage caused symptoms and was treated with placement of a stent as can be seen in the picture. Sometimes, bypass surgery is required in the setting of multiple severe blockages.
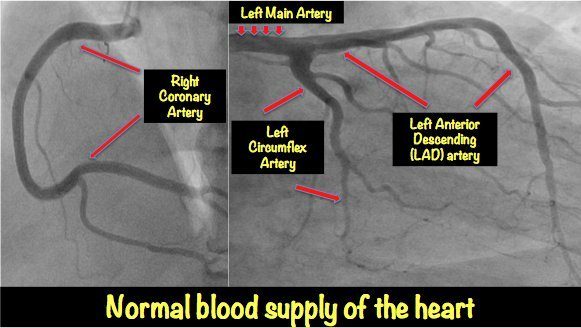
What are the three arteries that run over the surface of the heart?
There is one artery on the right side, and two arteries on the left side. The one on the right is known as the right coronary. On the left side, which is the main side, we have the left anterior descending (LAD) that runs down the front of the heart and supplies the front and main wall, and then the left circumflex that supplies the sidewall. If you look carefully, a major artery called the left main artery supplies the LAD and the circumflex. The left main artery and even the LAD artery are so important that critical blockages in these arteries are known as the Widow Maker!
Yes, You Can!
Dean Ornish, MD, founder and president of the Preventive Medicine Research Institute, has written six best-selling books, including Dr. Dean Ornish's Program for Reversing Heart Disease.
What It Takes
Ornish's plan includes walking at least half an hour a day, or for an hour three times a week. Yoga, meditation, and stress reduction are also involved.
Is It Too Strict?
You’ll need to be really motivated to make those changes, and to make them last.
Symptoms of Clogged Arteries
Clogged arteries are caused by atherosclerosis, which develops over time as plaques formed from fats, minerals, cholesterol, and more build up inside the walls of your arteries. These buildups cause the inner tunnels, called lumens, of the arteries to become smaller and narrower.
What Causes Clogged Arteries?
Clogged arteries are caused by a buildup of plaque in your arteries. Plaque is usually made up of a few substances, including minerals like calcium, or fats and cholesterol. High cholesterol levels can lead to this buildup of plaques.
Risk Factors for Clogged Arteries
A diet that is high in fats and cholesterol is just one of the things that can contribute to a buildup of plaques and clogged arteries.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing arterial problems may begin with your primary care doctor, but if a blockage is suspected, you will most likely be referred to a cardiologist or vascular specialist.
Treating Clogged Arteries
Treating clogged arteries should be done with a holistic approach. Your doctor will first address the problems that led to the clogged artery. Lifestyle changes are key, and may include:
Complications
The most concerning complications of clogged arteries are heart attack and stroke. A heart attack can occur when there is blockage in the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart. When a blockage affects the brain, this is called an ischemic stroke. This type of stroke can be treated effectively with strong blood thinners.
Prevention and Management
The key to keeping your arteries clear of blockages is to eat a low-fat diet and exercise regularly. Plant-based diets have even been shown to help reverse coronary artery disease in some people. 8
What to do if your arteries are blocked?
Instead, your doctor may suggest an invasive treatment to remove or bypass the blockages .
How to prevent cardiac problems?
Exercise can improve your cardiovascular health and help prevent cardiac issues. If you’re not physically active, start slowly. Go for a walk once or twice a week. When that fits into your schedule, go for more walks.
What happens if you have a plaque over your cholesterol?
In a worst-case scenario, cells form a plaque over the cholesterol, and a small blockage is formed. Sometimes they can break loose and cause a heart attack. As the plaques grow, they may block blood flow in an artery entirely.
How to heal plaque?
Eat a heart-healthy diet. Diet can play a big role in improving your heart health and reducing your risk for a buildup of plaque. It’s never too late to eat a healthier diet. Just as years of bad eating can damage your body, good eating can help heal it. A heart-healthy diet contains plenty of good fats and low amounts of bad fats.
How to lower LDL cholesterol?
Most artificial trans fats are found in processed, packaged foods like cookies and snack cakes. Increase your fiber intake. Soluble fiber helps lower your LDL. You can find soluble fiber in foods like vegetables, lentils, beans, and oats. Cut back on sugar.
How to reduce plaque in the heart?
Losing weight, exercising more, or eating less cholesterol-rich foods are all steps you can take to reduce plaques, but these steps won’t remove existing plaques. Focus on promoting better heart health by maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Healthy habits will help prevent additional plaque from forming.
How to get rid of a fatty stomach?
They’re found in foods like olives, nuts, avocado, and fish. Cut sources of saturated fat, such as fatty meat and dairy. Choose lean cuts of meat, and try eating more plant-based meals. Eliminate artificial sources of trans fats.

Clinical significance
Classification
Overview
Symptoms
Specialist to consult
Mechanism
- In people with heart block, also called AV block, the electrical signal that controls the heartbeat is partially or completely blocked from reaching the ventricles.
Signs and symptoms
- Heart block is classified as first-, second- or third-degree, depending on the extent of electrical signal impairment.
Causes
- Type I heart block (also called Mobitz Type I or Wenckebach's AV block) is the less serious form of second-degree heart block. In this condition, the electrical signal goes slower and slower until the heart actually skips a beat.