How to Support a Healthy Migrating Motor Complex
- Reduce Your Stress Levels. Studies show that stress messes with digestion. Stress can slow digestion down leading to constipation and a slowed MMC.
- Most Grown Ups Shouldn’t Snack. Remember that the MMC cycle is activated by having an empty stomach and naturally occurs every 90-120 minutes.
- Overnight Fast (don’t panic! this isn’t scary) A 12-hour (minimum) fast overnight allows the digestive system to take a break from constantly having to digest and process food.
- Vagus Nerve Support. The Vagus nerve is the longest nerve of the cranial nerves and runs from the brain throughout your body.
- Supplements^. There are many supplements and herbals that may assist in supporting the MMC. These are called prokinetics, and there are drugs that do a similar thing.
What is the migrating motor complex?
So what exactly is the migrating motor complex? The MMC is a cyclical pattern of electromechanical activity that is observed in the smooth muscle of the GI tract between meals. You can think of the MMC as a cleansing wave that sweeps the small intestines clean between meals.
What is the Migrating Motor Complex (MMC) deficiency?
Unless the MMC deficiency is addressed, no amount of herbs or pharmaceutical antibiotics will keep the small intestines clear. So what exactly is the migrating motor complex? The MMC is a cyclical pattern of electromechanical activity that is observed in the smooth muscle of the GI tract between meals.
What is Phase 3 of the migrating motor complex?
Phase III – Regular contractions in the antrum at 3 per minute, and in the small bowel at 11-13 per min complete the migrating motor complex. An MMC cycle lasts about 100 min, but depending on age may be more frequent in young children. Then a meal is given, and provocative medications if needed.
How can i Improve my MMC?
The MMC only sweeps the small intestines in periods of fasting between meals. MMC activity shuts down when we eat. By eating snacks or grazing between meals, you may be inhibiting you MMC function even more. Try to space out meals to increase MMC function. Intermittent fasting can be helpful for some case.

Does water affect migrating motor complex?
Manometric examination showed that the administration of mineral water induced a brief decrease of phasic motor activity, followed by a progressive increase, which in some cases ended in an activity front of the Migrating Motor Complex.
How do I know if my migrating motor complex is working?
When you hear the “growling” sound in your belly this is your migrating motor complex at work. The MMC doesn't just sweep food waste into the large intestine, but it also sweeps the small intestines clean of bacteria throughout the day.
What interrupts the migrating motor complex?
Abstract. The migrating motor complex (MMC) is a cyclic, recurring motility pattern that occurs in the stomach and small bowel during fasting; it is interrupted by feeding. The MMC is present in the gastrointestinal tract of many species, including humans.
What causes MMC dysfunction?
Autoimmunity following infection by a pathogen producing CdtB, such as C. jejuni, may be the leading cause of MMC impairment. Narcotics are also known to impair the MMC. Stress has been shown to reduce MMC activity as well.
How do you increase GI motility?
From Fuel to Stool: 5 Tips to Speed Up DigestionExercise for 30 minutes a day. Food and digested material is moved through the body by a series of muscle contractions. ... Eat more fiber. ... Eat yogurt. ... Eat less meat. ... Drink more water.
What foods should be avoided with SIBO?
What Foods Should Be Avoided With SIBO?Lentils and beans.Wheat and rye.Natural and artificial sweeteners, including agave syrup, xylitol, sorbitol, and high fructose corn syrup.Dairy products like cottage cheese or ice cream.Certain vegetables, including onions, garlic, artichokes, cabbage, and cauliflower.More items...
How long does the migrating motor complex last?
The migrating motor complex (MMC) serves the role of housekeeper of the small intestine by propelling undigested food residue and sloughed enterocytes. The MMC consists of four phases with a total duration of 84–112 min.
How long does the migrating motor complex take?
The migrating motor complex does its job in approximately 60 to 120-minute cycles, though some research indicates the process may take up to 90-230 minutes. It's a four-phase process consisting of different contraction rates in the stomach and small intestine that repeat until your next meal.
What hormone initiates the migrating motor complex?
Motilin and ghrelin are the gastrointestinal (GI) hormones released in a fasting state to stimulate the GI motility of the migrating motor complex (MMC).
What causes slow migrating motor complex?
Hypothyroid. Low thyroid function can affect all cells of the body, including the cells of the GI tract. Hypothyroid can reduce the activity within the gastrointestinal tract, slowing the migrating motor complexes that trigger peristalsis.
What is colonic migrating motor complex?
The colonic migrating motor complex (CMMC) is a critical neurally mediated rhythmic propulsive contraction observed in the large intestine of many mammals. It seems to be equivalent to the high amplitude propagating contractions (HAPCs) in humans.
What are natural Prokinetics?
Natural prokinetic agents include ginger, herbal bitters (eg, gentian root, dandelion root and leaf, burdock root), and a formulation called Iberogast.
What is the Migrating Motor Complex?
The migrating motor complex is an electromechanical process that occurs within the smooth muscle of the digestive tract. Often referred to as the "janitor" or "housekeeper" of the gut, the MMC's job is to move along left-over particles and substances in the digestive tract, to be rid of via our stool.
Why is it Important?
The MMC is a very important motility function, that helps to 'clean up the gut' of any residual substances that we don't want hanging around.
How to Support the Migrating Motor Complex
Meal spacing is one of the best ways to improve your migrating motor complex and allow it the time to do its job. As you just learned above, it can take approx. 90-120 minutes for the MMC to occur.
How to increase MMC?
By eating snacks or grazing between meals, you may be inhibiting you MMC function even more. Try to space out meals to increase MMC function. Intermittent fasting can be helpful for some case. Although, some people with hormone issues may want to steer clear of this approach and stick with three meals a day. 3.
What is the MMC function?
If you have a history of concussions or even have developed signs of neurodegeneration, you may need to address inflammation in the brain to boost MMC function. MMC activity is an autonomic function that is controlled by the brain.
What is the MMC in the GI tract?
So what exactly is the migrating motor complex? The MMC is a cyclical pattern of electromechanical activity that is observed in the smooth muscle of the GI tract between meals. You can think of the MMC as a cleansing wave that sweeps the small intestines clean between meals.
What are the things that inhibit MMC function?
12 Things that inhibit MMC function. 1. High levels of anti-CdtB and anti-vinculin antibodies. These are two antibodies that rise following a food poisoning event. When you have food poisoning, your immune system develops antibodies to fight the toxins produced by the micro-organisms that have invaded the body.
Does SIBO cause brain fog?
The real kicker is that chronic gut issues lead to brain issues. Datis Kharrazian, a brain and gut health expert) always says that if your gut is on fire, so is your brain. Many SIBO patients experience brain issues like poor concentration, memory decline, handwriting decline and brain fog.
What is the role of the migrating motor complex?
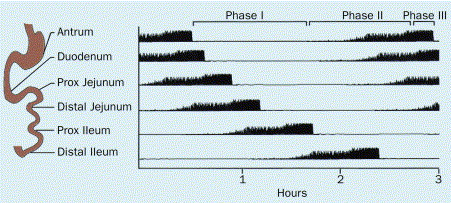
The migrating motor complex (MMC) serves the role of housekeeper of the small intestine by propelling undigested food residue and sloughed enterocytes. The MMC consists of four phases with a total duration of 84–112 min. Phase I is a period of motor quiescence lasting 40–60% of the cycle. Phase II, occupying 20–30% of the cycle, exhibits irregular phasic contractions. Phase III is a 5- to 10-min period of lumenally occlusive, rhythmic contractions occurring at the slow-wave frequency. Phase IV is a transitional period of irregular contractions between phase III and phase I. Seventy-one percent of phase III complexes originate in the stomach, 28% begin in the duodenum, and 1% originate in the proximal jejunum. Most MMCs terminate in the jejunum. MMC cycle duration is nearly twice as long if the previous phase III complex originated in the stomach versus the duodenum. Phase III contractions propagate over longer distances than those in phase II. The transit of inert substances is four times faster in phase III than in phase I and 50% of total flow occurs during phase III. On cineradiography, transit during phase III is characterized by intermittent boluses of 4–5 cm in length separated by 1- to 2-cm ring contractions.
How does a meal stop the moving motor complex?
A Meal Stops the Migrating Motor Complex. The MMC continues until it is terminated by the ingestion of food. Ingestion of a meal with sufficient caloric content halts the MMC. Termination requires contact of the meal with the upper digestive tract, because intravenous feeding does not end the fasting pattern.
What is the MMC cycle?
The migrating motor complex (MMC) is an organized fasting pattern that propels undigested food residue and sloughed enterocytes from the proximal gut; it has been termed the intestinal housekeeper ( 142 ). Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth develops rapidly in rats given morphine to disrupt MMC cycling, which shows the importance of the complex ( 143 ). The electrical correlate of the MMC is the migrating myoelectric complex ( 144 ). The MMC consists of four phases with a total duration of 84 to 112 minutes ( Fig. 38-4 ). Phase I is a period of motor quiescence lasting 40% to 60% of the cycle length. Phase II, occupying 20% to 30% of the cycle, exhibits irregular phasic contractions involving approximately half of slow wave cycles. The duodenal cross-sectional area is greater during phase II than phase I, possibly serving to accommodate pancreaticobiliary secretions ( 145 ). Phase III is a 5- to 10-minute period of luminally occlusive, rhythmic contractions, most of which propagate aborally. However, some duodenal phase III contractions propagate in an orad direction, indicative of a physiologic retroperistaltic pump ( 146 ). This retroperistaltic activity is associated with duodenogastric reflux of bicarbonate and immunoglobulin A, which have been proposed to reconstitute the antral mucosal barrier during fasting ( 147 ). Retrograde duodenal motor activity during late phase III directed against antral phase III pressure waves also may increase fasting duodenal pH and nocturnal antral pH, serving to protect both regions ( 148, 149 ). Finally, up to 32% of phase II pressure waves are bidirectional ( 148, 149 ). The maximal phase III contractile frequency is determined by the slow-wave frequency (11–12 cycles/min in the duodenum, 7–8 cycles/min in the ileum). Phase III complexes propagate more slowly (4–6 cm/min) than the slow wave because of a loss of slow-wave phase locking and shortening of frequency plateaus ( 150 ). Nevertheless, individual phase III contractions propagate over longer distances than phase II contractions ( 108 ). The length of intestine in a given phase III complex decreases from 40 to 60 cm in the duodenum to 5 to 10 cm in the ileum. Phase IV is a transition period of irregular contractions occurring between phases III and I.
What is the MMC influenced by?
The MMC is influenced by extrinsic and intrinsic neural sources. Bilateral vagotomy, removal of the superior and inferior mesenteric ganglia, total sympathectomy, and complete extrinsic denervation do not prevent MMC cycling, although cycle duration and regularity may be altered.
Where do MMCs end?
Most MMCs terminate in the jejunum. MMC cycle duration is nearly twice as long if the previous phase III complex originated in the stomach versus the duodenum. Phase III contractions propagate over longer distances than those in phase II.
Which regions of the brain are able to initiate MMC?
Both the central and peripheral neural regions are also able to initiate MMC. For example, MMC can commence peripherally in any regions of the small intestine when the central mechanisms are inactive [27]. In addition, MMC is also controlled by gut hormones such as motilin [24].
Where does MMC occur?
Nevertheless, this effect occurs only in the stomach and upper small intestine, not in the ileum. The MMC is one of the motor programs in the program library of the enteric nervous system and requires that the enteric nervous system be fully functional. The MMC continues in the small intestine after interruption of all inputs from ...
How to get rid of a broken vagus?
1.Exercise your Vagus! Just like your muscles, neurons need constant stimulation to stay healthy and strong. If you break a bone and wear a cast for 6 weeks, it is almost shocking to see the muscle loss when they remove the cast. Because we didn’t use that muscle in 6 weeks it starts to waste away and lose its function. In the same way, neurons will start to lose their function if we aren’t actively working them out.
How to help gut brain axis?
Eat a whole foods anti-inflammatory diet. When you are having a problem with your gut brain axis it becomes imperative to remove processed foods from your diet and to increase your consumption of nutrient dense whole foods. Fruits and vegetables are filled with phytonutrients that can help calm systemic inflammation.
What happens when the vagus nerve is activated?
The brains ability to activate the vagus nerve will then become blunted by the inflammation in the brain, which will reduce blood flow, nutrients, enzyme release and motility in the gut leading to more inflammation in the gut! The process becomes a very vicious cycle of inflammation and dysfunction.
How does the MMC cycle vary?
The length of the MMC cycle appears to vary between individuals and can vary on a daily basis. The duration of the cycle also seems to be dependant on the origin of phase 3 (stomach or small intestine) and on the intragastric pH level. The more acidic the pH, the longer duration of the MMC.
What is the most active phase of the MMC cycle?
Phase 3 is the most active and powerful phase, where 2-3 contractions per minute are present in the stomach and 11-12 contractions per minute are present in the small intestine. Phase 4 mimics phase 2. After phase 4, phase 1 begins again, unless disrupted by food intake from the next meal or snack. The length of the MMC cycle appears ...
How to increase space between meals and snacks?
To increase space between meals and snacks, ensure they are well-balanced and contain fiber and healthy fats for increased satiety over longer periods of time. If the MMC function is disordered, a prokinetic agent can be helpful. This is typically used for those with SIBO and chronic constipation.
Where is motilin produced?
Motilin is produced by endocrine cells of the proximal small intestine, and levels are shown to peak just before phase 3 of the MMC begins. This only happens with gastric-onset phase 3 contractions. Research suggests that the motilin-induced phase 3 contractions may signal hunger. The MMC is also thought to be regulated by ...
What is the MMC in the body?
The migrating motor complex (MMC) is one of our body’s most important mechanisms for proper digestion. This mechanism refers to the periodic mobility pattern that occurs in the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract, including the stomach and small intestine, during the fasting state.
