
Benfotiamine or vitamin B1 helps the olfactory nerve already weakened by excessive alcohol consumption, too much sugar, diabetes, and others ailments. Choose a liposoluble benfotiamine (#ad) so that the vitamin more easily penetrates the nerves and begins to repair them. The recommended dose is 100mg a day.
What happens if the olfactory nerve is damaged?
Damage to the olfactory nerve can result in three different disorders. The first, anosmia is an inability to smell at all. Some people with olfactory nerve damage develop anosmia, but some simply have a reduced ability to smell. This is called hyposmia.
How to speed up olfactory nerve recovery?
Such bugs hinder olfactory nerve improvements by their harmfulness effects on the neurons. Thus, in before said damages, function of olfactory nerve is impaired and leading to anosmia. For a better recovery, administering anti inflammatory medications such corticosteroid may speed up anosmia restoration [ 5 ].
What is the function of the olfactory nerve Quizlet?
Function of the Olfactory Nerve. The olfactory nerve is responsible for your sense of smell and partially responsible for your sense of taste. It is also known as cranial nerve 1 because it is the shortest of the cranial nerves and one of only two nerves (the other is the optic nerve) that bypass the brain stem and connect directly to your brain.
What is the prognosis of olfactory nerve transection?
Recovery following olfactory nerve transection also depends on the degree of injury. Extensive lesions involving damage to both the olfactory nerves and layers of the olfactory bulb are more likely to produce scar tissue and gliosis, introducing mechanical barriers to axon growth.
Where does the olfactory nerve begin?
What are the disorders of the olfactory system?
What happens when the cribriform plate is broken?
Why do people lose their sense of smell?
What are the cells that make up the nose called?
Which nerve is responsible for taste?
Can olfactory nerve damage cause smells?
See more
About this website

Can damaged olfactory nerves be repaired?
Unlike nerve cells anywhere else in the body, the olfactory neurons are able to recover or regenerate after injury.
What helps olfactory neurons regenerate?
Vitamins and minerals are essential for healthy nervous system. Vitamin A helps to form and maintain healthy body structures and has recently been shown to play a role in the regeneration of olfactory receptor neurons.
How do you stimulate olfactory neurons?
Carry a vial of a nonirritating substance in your bag; vanilla, lemon, and freshly ground coffee are good examples, and tobacco or scented soap will do if necessary. These odors stimulate the olfactory receptors. Do not use irritating odors such as camphor or menthol.
How long does it take for olfactory nerve to regenerate?
Research has shown that each regenerating olfactory axon can follow the pathway created by pre-existing axons every 30–90 days.
What vitamins help regenerate olfactory nerves?
Vitamin A plays a decisive role in the regeneration of olfactory receptor neurons. In this retrospective study we investigated the effectiveness of topical vitamin A in patients with post-infectious and posttraumatic smell disorders.
How do you repair olfactory nerve after Covid?
Training the nose The mainstay of treatment for post-COVID smell loss is olfactory training — a procedure that many rhinologists compare to physical therapy for the nose.
Is loss of sense of smell curable?
There is currently no known cure for congenital anosmia. In most cases, however, anosmia goes away on its own. Generally, once the underlying problem is treated, your sense of smell is restored.
How do I reset my smell and taste after Covid?
What you can do to helplearn about your condition from trustworthy sources.eat cool or room temperature foods.take small mouthfuls – don't give up too quickly as you may get used to the taste.try bland foods like rice, boiled potatoes and pasta.try flavours that appeal to you.More items...•
Is loss of smell permanent?
In most cases, the smell loss lasts only a few weeks, but for more than 12 percent of people with COVID-19, olfactory dysfunction persists in the form of ongoing reduction in the ability to smell (hyposmia) or changes in how a person perceives the same smell (parosmia).
Do olfactory cells grow back?
Olfactory epithelial cells are also among the fastest growing and regenerating cells in the body. Olfactory epithelial cells, unlike taste bud cells, regenerate in a variety of time frames, from every 24 hours to days and weeks.
How do you promote neuron regeneration?
Continuous training (slow walking at 10 meters/min for one hour per day) was effective in promoting nerve regeneration in males but not females and interval training (four repetitions of short sprints at 20 meters/min for 2 minutes following by 5 minutes of rest) was effective in females and not males.
What happens if the olfactory nerve is damaged?
A damaged sense of olfaction is severely disrupting: the joy of eating and drinking may be lost, and depression may result. Furthermore, there are dangers associated with the loss of smell, including the inability to detect leaking gas or spoiled food.
How do you stimulate an olfactory bulb?
Build your scent IQ The researchers added that people with an average sense of smell can increase the size of their olfactory bulbs with a regimen of trying out four aromas, twice a day, for about 30 seconds each.
Do olfactory cells grow back?
Olfactory epithelial cells are also among the fastest growing and regenerating cells in the body. Olfactory epithelial cells, unlike taste bud cells, regenerate in a variety of time frames, from every 24 hours to days and weeks.
What happens when the olfactory nerve is damaged?
A damaged sense of olfaction is severely disrupting: the joy of eating and drinking may be lost, and depression may result. Furthermore, there are dangers associated with the loss of smell, including the inability to detect leaking gas or spoiled food.
What causes olfactory nerve damage?
The principal causes of olfactory dysfunction are sinonasal diseases, viral infections, head injuries, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Olfactory Nerve Regeneration Time Period after the Damage
Case Report - Otolaryngology Online Journal (2020) Volume 10, Issue 6. Olfactory Nerve Regeneration Time Period after the Damage Hashem Shemshadi*
Olfactory Nerve: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment
Dysosmia: Dysosmia can cause a distortion in how you perceive an actual odor, or it can cause phantom smells—odors that aren't actually there.This is called an olfactory hallucination. In most cases, this is due to degeneration of the olfactory epithelium. Anosmia: Anosmia is the total loss of the sense of smell.It can be caused by infection, blockage, or head injury.
Taste and smell — the olfactory nerve & the five senses | HC Smart
Address: 20900 NE 30th Ave, Ste 200, Aventura, FL 33180 Fax: 305-421-7284 [email protected]
Post-Traumatic Olfactory Loss - Fifth Sense
As the names suggests, post-traumatic olfactory loss describes anosmia or hyposmia which results from a head injury. The extent of loss is determined not only the severity of the injury but also the part of the head damaged; smell loss is more likely to occur from injuries to the back of the head.
What is the function of the olfactory nerve?
Associated Conditions. Treatment. Actually a pair of cranial nerves, the olfactory nerve transmits information to the brain from smell receptors in the nose. The olfactory nerve is sometimes referred to as the first cranial nerve, or CN1. Cranial means "of the skull.".
Where is the olfactory nerve located?
That might seem odd since the olfactory nerves are in the front of the brain. When there's an impact on the back of the head, the brain can come forward and collide with the inside front of the skull—right where the olfactory nerve is.
What nerve is responsible for smell?
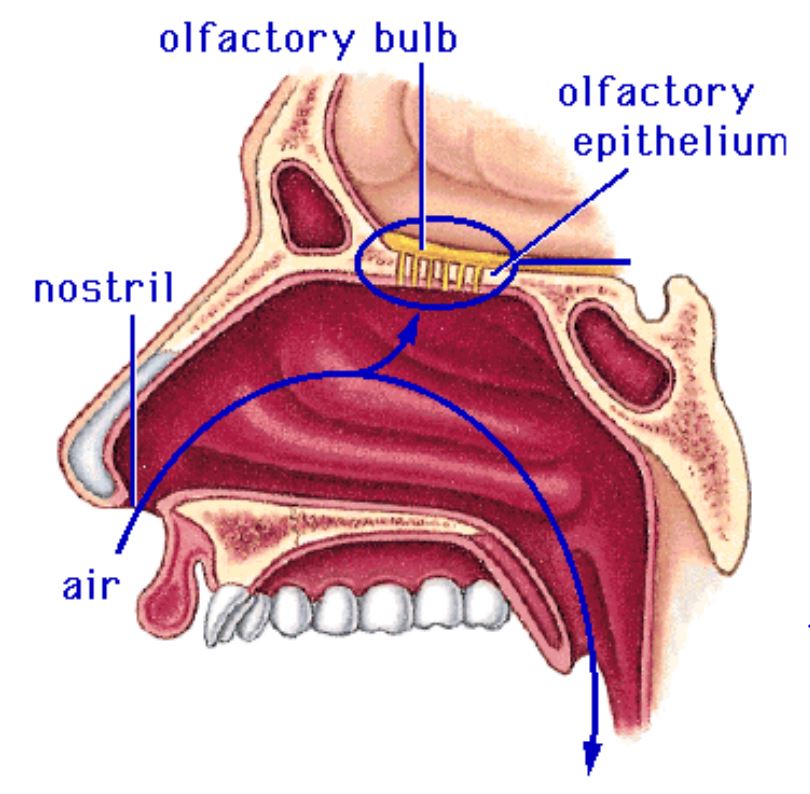
Unlike many other nerves, the olfactory nerve has one job—making you able to smell things. When particles in the air enter your nasal cavity, they interact with the receptors on the olfactory nerve and a type of tissue called the olfactory epithelium, which is in several areas of the nasal cavity and contains millions of receptors.
Why does my sense of smell decrease?
A decreased sense of smell can also occur due to tumors, such as meningiomas of the olfactory groove as well as be an early feature of some neurological diseases such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and Lewy body dementia.
Why does my smell go away?
The olfactory nerves can become severed in this way, but often the smell loss is due to bruising of the olfactory bulb.
How often do you lose smell sensitivity?
In others, it's a gradual loss over the course of several acute illnesses which most people get a few times a year.
Where does the nasal nerve originate?
It originates in the olfactory mucosa (mucous membrane) along the roof of your nasal cavity (nostril). This nerve is made of many small nerve fibers called fascicles that are bound together by thin strips of connective tissue. The bundle extends from the nasal cavity through the ethmoid bone behind your nose.
What is the role of insulin in the development of olfactory neurons?
Researchers have known for some time that insulin plays a vital role in regeneration and growth in some types of neurons that relay environmental sensory information to our brains, such as sight.
What is an odor-guided behavioral task?
An odor-guided behavioral task, in which the mice needed to find a cookie reward depending on their ability to smell, measured olfactory function. In addition, the team injured OSNs, which have a unique ability to regenerate in mammals.
How long does it take for OSNs to regenerate after injury?
These results indicate that insulin facilitates the regeneration of OSNs after injury and suggest a critical stage during recovery (8 – 13 days after injury) during which the maturation of newly generated OSNs is highly dependent on and promoted by insulin.
Does reduced insulin affect the sense of smell?
The reduced insulin interfered with the regeneration of OSNs, resulting in an impaired sense of smell. They analyzed how the structure of the olfactory tissue in the nasal cavity and the olfactory bulb is impaired by comparing the number of mature OSNs and how well the axons of OSNs reached the olfactory bulb.
Does insulin help with OSNs?
Knowing that insulin is part of the body’s repair pathway for visual neurons, Kuboki suspected that the hormone might also play a role in the maturation of OSNs after injury. He also notes there are many insulin receptors in the olfactory region of the brain. Taking these factors into account, Kuboki concluded that insulin may also be involved in ...
Does insulin affect olfactory neurons?
Although insulin receptor signaling is known to have an influence on cellular processes such as proliferation and apoptosis, it is poorly understood whether the insulin influences the regeneration of olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) after injury.
Why does the olfactory nerve lose its neurotoxin strength?
Olfactory nerve due to previously mentioned issue loses their neurotoxin strength to attract chemical particles. Chemical adhesion effects diminish. Thus, as a nelderly, one not feels these sence of materials well as the same quality of previous years [ 9 ]. Congenital anosmia is another reason for not being able to smell well since birth [ 10 ].
When does anosmia recover?
Modest source of anosmia such as a common cold, rhinitis and rhino sinusitis recovery is as soon as the patient convalesces from the disease course [ 2 ].
What causes anosmia?
Using and abnormal exposures to chemicals and smokes, may also contribute to anosmia. Improving their anosmia due to the above named causes is to turn off their exposure within an effective time interval in exposing to the above said substances [ 7, 8 ].
What viruses cause anosmia?
Neurotrophic viruses, which inhibit nervous system progression, also may contribute to anosmia. These viruses apparently are more atypical and or more aggressive in comparison to other viruses. Such bugs hinder olfactory nerve improvements by their harmfulness effects on the neurons.
What is the reason for the decline of smell?
Aging is another factor in declining the function of smelling. Like all other parts of the body which get weak by the passing of time, lowering neurophysiological functions are not excluded during this journey.
Is rhinoplasty a non-emergency trauma?
Different therapeutic modalities have been intervened with low and /or no satisfactory results [ 11 ]. Post rhinoplasties in form of primary cosmetic, secondary reconstruction and any nasal surgery manipulation, is considered as a non-emergency trauma to the olfactory nerve [ 12 ]. In latter mentioned reference, an osmia returned into normal value, within 6 months post operatively.
Is anosmia a clinical indicator?
Referable to the virus rigorousness and its nontypicality, it is currently assume d, presenting with anosmia, may be employed as an assisting clinical indicator for patients who have the COVID-19 disease [ 6 ]. Still ongoing publications and suggestions for a better preventing, diagnosing and treating above mentioned viral disease, arriving on world-widely. Proper medication and its effective vaccine are also are debated comprehensively.
What is the role of axons in olfactory development?
During olfactory development axons from the sensory epithelium migrate to the olfactory bulb and gradually establish connections with targeted glomeruli ( Key and St John, 2002 ). The spatial distribution of these connections form the basis of a topographical mapping of odorant receptors onto the olfactory bulb ( Vassar et al., 1994 ). The olfactory epithelium retains its capacity to undergo neurogenesis long after development and odorant receptors continue to establish new connections in the adult olfactory bulb. Remarkably, these newly rewired connections converge onto glomeruli in specific areas of the bulb maintaining a topographical mapping of odorant receptors. The preservation of this spatial mapping of odorant receptors onto the olfactory bulb plays an essential role in the processing of olfactory information while disruption of odorant maps results in impaired or altered olfactory function ( Yee and Costanzo, 1998 ).
When the olfactory nerves and bulbs are injured, must axons find new pathways or?
When the olfactory nerves and bulbs are injured, regenerated axons must find new pathways or overcome barriers such as gliosis and the formation of scar tissue before they can reestablish connections with the bulb.
What is the inability of axons to rewire the olfactory bulb?
The inability of axons to accurately rewire the olfactory bulb and restore the spatial integrity of odorant receptor maps is more likely to occur following injury to the olfactory nerves and bulbs than to the neuroepithelium.
What are the causes of scar tissue in the olfactory bulb?
Extensive lesions involving damage to both the olfactory nerves and layers of the olfactory bulb are more likely to produce scar tissue and gliosis, introducing mechanical barriers to axon growth. Regenerating axons must penetrate or circumvent these obstacles if they are to successfully rewire the olfactory bulb.
What is the olfactory system?
The olfactory system has become a popular model for the study of neural regeneration and the rewiring of axons following injury. Lesions to the neuroepithelium, nerve fibers and olfactory bulb all have disruptive effects on odorant receptor mapping. Regeneration and the restoration of olfactory receptor connections depend upon ...
What are the mechanisms that facilitate or inhibit the guidance of axons to specific targets in the ol?
Mechanisms that facilitate or inhibit the guidance of axons to specific targets in the olfactory bulb are topics of considerable interest. Axon–cell interactions, growth factors, the role of glia cells and axonal outgrowth and interaction with extracellular matrix molecules are all topics that need further investigation.
What instruments were used to study olfactory nerve lesions?
Early studies of olfactory nerve lesions used metal blade instruments. This often resulted in extensive damage to multiple layers of the olfactory bulb as well as the scraping of bone and dura along the cribriform plate.
How to get your sense of smell back?
If a sinus infection or other illness has temporarily dulled your sense of smell, you can restore it faster through olfactory training. Sniff something with a strong fragrance for a few minutes several times a day , and you’ll help your system create new neural pathways for heightened smell sensitivity.
How to improve your ability to smell?
1. Reestablish Your Baseline with Scent Elimination Exercises. One way to enhance your ability to smell is by taking strong scents out of your life—at least temporarily. Our noses become sensitized to daily smells over time to the point we no longer notice them.
How many people over 40 have a smell problem?
You’re not alone if you feel less sensitive to smells. An estimated one in four people over 40 deals with smell-related issues. These include hyposmia (partial loss of smell) and anosmia (complete loss of smell). The actual percentage could be much higher, as smell research largely depends on self-reporting.
What causes a person to lose their sense of smell?
Dental Problems: Oral health issues like gingivitis and gum disease can harm your sense of taste and smell. Age: You start to lose olfactory nerve fibers in your nose as you age, and 12% of adults over 40 experienced some form of smell disfunction. Disease: Cancer, dementia, Parkinson’s disease, and dozens of other chronic health problems may ...
What to eat if you don't like the smell of food?
If you find yourself not tasting dinner as well, fill your plate with foods like beans, shellfish, salmon, tuna, seeds, nuts, dairy products, beef, liver, and even fortified cereals.
Why is it important to have a working nose?
Without a working nose, you can’t tell whether food is spoiled by taste, detect body odor, recall scent-related memories, or even know whether your home is filling with smoke or other toxins.
What vitamins are bad for your sense of smell?
Sometimes the medications used to treat them include loss of smell as a side effect. Vitamin Deficiencies: A lack of vitamins such as A, B6, B12, and zinc are associated with a diminished sense of smell.
What is the function of olfactory sensory neurons?
Olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) are nasal neurons that make use of hundreds of different types of odorant receptors to analyze odorous chemicals in our external world and send that information to our brain.
Does odor stimulation affect regeneration?
The paper, out today from the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus and published in Cell Reports, explores whether this process has a function beyond just replacement. After lessening odors though one side of the nose, researchers examined the birth rates of different subtypes of OSNs in mice to determine how odor stimulation can affect the regeneration process. Results show that diminished odor stimulation reduces the number of newly-generated neurons that express particular odorant receptors, indicating a selective alteration in the neurogenesis of these neuron subtypes.
What happens to the olfactory neurons after injury?
However, damage sustained in the injury can lead to the development of scar tissue which can prevent the axons reaching the bulb.
Where is the olfactory system located?
The olfactory system is situated at the lower-front of the brain and is therefore very susceptible to damage in this way. People who have suffered a loss of smell in this way may have been told that the olfactory loss has been caused by the olfactory nerves being severed.
Why is smell training important?
Smell training can help you to firstly establish whether you are able to detect any odours and then maximise any olfactory ability that does remain. It is certainly worth trying and we also feel there is an element of self-empowerment in doing this, particualrly if you’ve been told that nothing can be done by your doctor.
What is post traumatic olfactory loss?
What is post-traumatic olfactory loss and what causes it? As the names suggests, post-traumatic olfactory loss describes anosmia or hyposmia which results from a head injury. The extent of loss is determined not only the severity of the injury but also the part of the head damaged; smell loss is more likely to occur from injuries to the back ...
Why does my nose smell bad?
Smell loss can result from damage to the front of the head or face too. For example, direct injury to the nose can prevent odours travelling to the olfactory cleft, the space at the top of the nose where the receptor cells are located.
Why did Molly lose her sense of smell?
After losing her sense of smell as the result of a head injury Molly set off on a journey to try to regain it and learn more about her condition and the the sense of smell itself. Highly recommended reading for anyone affected by post-traumatic olfactory loss.
Where do olfactory receptors travel?
They travel from the olfactory receptor cells through a layer of bone in the skull called the cribriform plate which is covered in tiny holes, almost like a sieve. As the brain bounces back and forth as described above the nerves fibres can be pulled and snag on the edges of the holes in the bone and break.
How to regain sense of smell?
Zinc is an essential mineral for maintaining the senses of taste and smell.
Which nerve controls the sense of smell?
Unfortunately, most neurologists test overall neurological function and omit the cranial nerve that controls the sense of smell.
Why is smell a traumatic brain injury?
It is the result of a traumatic brain injury because the nerve that controls smell, the olfactory nerve, is located behind the ear, at proximity to the surface and is thus exposed to possible trauma.
How to regain normal perception?
To regain your normal perception, it is essential to restore this zinc level and to accumulate it for a while through appropriate supplementation while carrying out olfactory rehabilitation to reprogram the brain.
Why do you need liposoluble benfotiamine?
Choose a liposoluble benfotiamine (#ad) so that the vitamin more easily penetrates the nerves and begins to repair them.
Why does anosmia last for months?
Persistent anosmia over months would also be caused by damage to these stem cells impacted by the virus.
What is the mineral that helps you taste and smell?
Zinc is an essential mineral for maintaining the senses of taste and smell.
Where does the olfactory nerve begin?
The olfactory nerve begins in the region of the nasal cavity known as the olfactory epi thelium. The epithelial cells there are covered with tiny hairs called cilia on one side, and they are connected to an axon, which is the main body of a nerve cell, on the other side.
What are the disorders of the olfactory system?
Disorders of the olfactory system include anosmia (an inability to smell), hyposmia (a reduced ability to smell), and dysosmia (a distortion of your perception of a smell). To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account.
What happens when the cribriform plate is broken?
This often happens when the cribriform plate is broken, severing the axons of the olfactory nerve. Even if the cribriform plate is not broken, a blow to the head or face can damage these delicate cells and result in a partial or total loss of smell.
Why do people lose their sense of smell?
In addition, most people gradually lose some of their sense of smell as they get older. We don't really know exactly why this happens, but it is thought that after many years of damage from viral infections and small traumas, the epithelial cells lose their sensitivity. This is not typically a total loss of smell, but damage to the olfactory nerve means that elderly people typically cannot detect odors as well as young people.
What are the cells that make up the nose called?
The cells there, called olfactory epithelial cells , are very specialized. On the side facing your nasal cavity (and so exposed to the smell-inducing chemicals), they are covered with tiny hairs called cilia, and on the other side, they are connected to an axon, which is the main body of a nerve cell.
Which nerve is responsible for taste?
The olfactory nerve is responsible for your sense of smell and partially responsible for your sense of taste. It is also known as cranial nerve 1 because it is the shortest of the cranial nerves and one of only two nerves (the other is the optic nerve) that bypass the brain stem and connect directly to your brain.
Can olfactory nerve damage cause smells?
Some people with olfactory nerve damage develop anosmia, but some simply have a reduced ability to smell. This is called hyposmia. Finally, olfactory nerve disorders can cause people to develop dysosmia, where smells are mixed up so that a pleasant aroma like that of a rose might smell bad, like rotting garbage.
Olfactory Nerve Regeneration Time Period After The Damage
Abstract
Introduction
Discussion/Conclusion
- If you've lost your sense of smell to a known cause that's treatable—such as by surgically removing nasal polyps, straightening the septum, or clearing out the sinuses—it's possible that your sense of smell will improve over time. That's what happens in many cases of post-viral olfactory loss, although the sense may never be fully restored. A study...
References
- University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences, Rofeideh Rehabilitation Hospital, Tehran, Iran *Corresponding Author: 1. Hashem Shemshadi University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences Rofeideh Rehabilitation Hospital, Tehran, Iran Tel: +98 912 1155618 E-mail: [email protected] or [email protected] Received: May 04, 2020; ...