
Medication
Our treatment options include:
- traditional open surgical repair options,
- minimally invasive surgical repair, and
- endovascular procedures.
Procedures
dr. glotzbach: it could, and once you've had an aortic dissection your aorta's at risk for life and so this is something that is, you know, can be managed and stable and people can go on living with it but it's not something that will ever heal completely and so people just have to be aware that they need lifelong surveillance and i think that's …
Nutrition
Aortic dissection is life threatening. The condition can be managed with surgery if it is done before the aorta ruptures. Less than one half of people with a ruptured aorta survive. Those who survive will need lifelong, aggressive treatment of high blood pressure.
See more
Medical management of Aortic dissection is usually focused in lowering blood pressure and reducing shear-force dP/dt. For this reason, vasodilators combined with a beta blocker is used to reduce shear stress. Calcium channel blockers are also effective in treating Aortic dissection.
What is the best treatment for aortic dissection?
Can an aortic dissection heal on its own?
How serious is aortic dissection?
Is there any natural treatment for aortic dissection?
See more
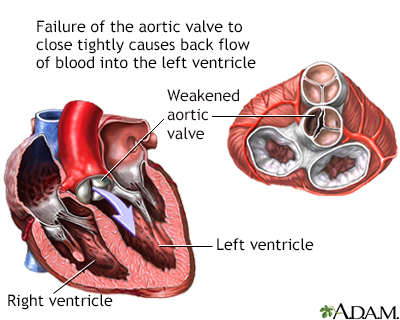
What is life expectancy after aortic dissection surgery?
1 Introduction. Acute type A aortic dissection (AAD) is a life-threatening emergency that carries a high mortality rate without surgical treatment [1,2]. Surgical mortality has been estimated to range from 9% to 30%, and survival rates of 51–82% at 5 years have been reported [3–9].
Can aortic dissection be saved?
Aortic dissection is relatively uncommon. It usually occurs in men in their 60s and 70s. Symptoms of aortic dissection may mimic those of other diseases, often leading to delays in diagnosis. However, when an aortic dissection is detected early and treated promptly, the chance of survival greatly improves.
Can an aortic dissection heal on its own?
The dissection may slowly heal on its own or cause a rupture in the aortic wall. Depending on the size, such a rupture can kill someone instantly or within a couple of days.
How long does an aortic dissection repair take?
A typical open-heart procedure takes from 4 to 6 hours, in some cases up to 8 hours; patients are then maintained under general anesthesia for an additional 4 to 6 hours.
Is aortic dissection instant death?
As many as 40 percent of people who suffer from an aortic dissection die almost instantly, and the risk of death increases by 3-4 percent every hour the condition is left untreated.
How many people survive aortic dissections?
Prognosis for Aortic Dissection Hospital mortality rate for treated patients is about 30% for proximal dissection and 10% for distal. For treated patients who survive the acute episode, survival rate is about 60% at 5 years and 40% at 10 years.
Can you live a normal life after an aortic dissection?
Post-dissection, many patients wonder when it is appropriate to return to their previous lifestyle. With excellent blood pressure control and conscious limits to physical activity, you can continue to live a long, full life after a dissection. This would include returning to most jobs.
Can coughing cause aortic dissection?
Chronic cough has a wide differential, of which thoracic aortic aneurysm is a rare but potentially devastating cause.
How serious is aortic dissection surgery?
Aortic dissection is a very complicated condition. Untreated, an aortic dissection can lead to death. A dissection that involves the ascending aorta almost always requires emergency open-heart surgery to repair the vessel and prevent death.
What is life expectancy after AAA repair?
After ruptured AAA repair, crude 5-year survival was 41.7% (99% CI, 39.6 to 43.7) and relative 5-year survival was 87.1% (99% CI, 83.9 to 90.3). No significant differences in relative 5-year survival were observed between time periods, sex, or age groups.
How serious is a aorta surgery?
Both open surgery and endovascular surgery can lead to serious complications. Some people also die as a result of surgery. The risk of dying within 30 days of surgery is higher in people who have open surgery than it is in people who have endovascular surgery.
Can you survive an aortic dissection without surgery?
The well-known complications of acute type A aortic dissection, for example, intrapericardial rupture, acute aortic valve insufficiency, coronary ischemia, and branch vessel occlusion, are often lethal without prompt surgical intervention.
Can you recover from a torn aorta?
An aortic dissection can be life-threatening if it is on the ascending aorta. This is the part of the aorta that goes up through your chest toward your head. A surgeon must repair this as soon as possible. There are 2 possible surgery methods for aortic dissection repair.
When is surgical repair of an aortic dissection advisable?
An aortic dissection —a split, tear, or weakened area in the lining of your body's main artery—is often a life-threatening condition and represents one of the rare true emergencies in cardiac surgery. Medication can sometimes be an appropriate treatment option for a dissection of the descending aorta.
How is repair of an aortic dissection accomplished?
There are a number of ways to repair or replace the portion of an aorta damaged by a dissection. Which option is used will depend on such factors as where the dissection is located, how much of your aorta needs to be repaired or replaced, and the overall state of your health.
What are the risks and benefits of such surgery?
It is important to keep in mind that every medical choice involves a trade-off between risks and benefits—whether it is to undergo surgery, take medication, or even just carefully monitor a condition (an option known as "watchful waiting").
What is involved in a typical recovery?
A typical open-heart procedure takes from 4 to 6 hours, in some cases up to 8 hours; patients are then maintained under general anesthesia for an additional 4 to 6 hours. If their heart is performing well and there is no excess bleeding, they can emerge from anesthesia and have their breathing tube removed.
How to diagnose aortic dissection?
Tests to diagnose aortic dissection include: 1 Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE). This test uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart in motion. A TEE is a special type of echocardiogram in which an ultrasound probe (transducer) is guided through your esophagus and placed close to your heart. This test gives your doctor a clearer picture of your heart and aorta than would a regular echocardiogram. 2 Computerized tomography (CT) scan of the chest. X-ray are used to produce cross-sectional images of the body. A CT of the chest can confirm a diagnosis of aortic dissection. 3 Magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA). An MRA uses a magnetic field and radio wave energy to create images of your blood vessels.
What are the symptoms of aortic dissection?
Doctors often suspect an aortic dissection if the following signs and symptoms are present: Sudden tearing or ripping chest pain. Widening of the aorta on chest X-ray. Blood pressure difference between right and left arms. Although these signs and symptoms suggest aortic dissection, more-sensitive imaging techniques are needed.
What medications can help with aortic dissection?
Some medications, such as beta blockers and nitroprusside (Nitropress), reduce heart rate and lower blood pressure, which can prevent the aortic dissection from worsening. They may be given to people with type A aortic dissection to stabilize blood pressure before surgery.
What is the purpose of a stent in the aorta?
Sometimes stents — small wire mesh tubes that act as a sort of scaffolding — may be placed in the aorta to repair complicated type B aortic dissections. After treatment, you may need to take blood pressure lowering medication for life.
Can you have a type A aortic dissection without surgery?
The same medications that are used to treat type A aortic dissection may be used without surgery to treat type B aortic dissections. Surgery. The procedure is similar to that used to correct a type A aortic dissection.
