Repairs are performed via arthroscopy (keyhole surgery). Repair of the meniscus root involves passing stitches into the meniscus remnant, and re-anchoring it to the bone.
What happens if you leave a torn meniscus untreated?
- Meniscus – It acts like a shock absorber for your knees and it’s located just between the tibia and femur. ...
- Ligaments – All the bones in our body are joined with ligaments. ...
- Tendons – Your muscles are connected with bones by tendons. ...
- Collateral ligaments – Collateral ligaments are found at the side of your knees. ...
How to heal a torn meniscus without surgery?
Treating a Torn Meniscus Without Surgery
- Your Knees and Your Menisci. The knee is a hinge joint. ...
- Nonsurgical Treatment for a Torn Meniscus. Your orthopedic doctor will consider your precise symptoms before deciding whether conservative (nonsurgical) treatment will work and will also factor in if your knee ...
- Orthopedic Doctor in the Triangle. ...
What are the best exercises for a meniscus tear?
Physical Therapy Exercises for a Knee Meniscus Tear
- Knee Range of Motion Exercises. Your knee meniscus tear may cause you to have limited knee range of motion. ...
- Quadriceps Exercises. Your quadriceps muscle, or "the quad," straightens your knee, and it supports the joint and your kneecap.
- Straight Leg Raises. ...
- Balance and Proprioception. ...
- Plyometrics and Neuromuscular Training. ...
- Bicycling. ...
What is the recovery time for meniscus surgery?
Some of the aspects that determine the recovery period are:-
- Severity of injury
- Age
- Health Status
- Dedication to follow the therapy

Can a meniscus root tear heal without surgery?
The options for treatment of meniscus root tears are either nonoperative management with physical therapy and/or injections or operative management.
How serious is a meniscus root tear?
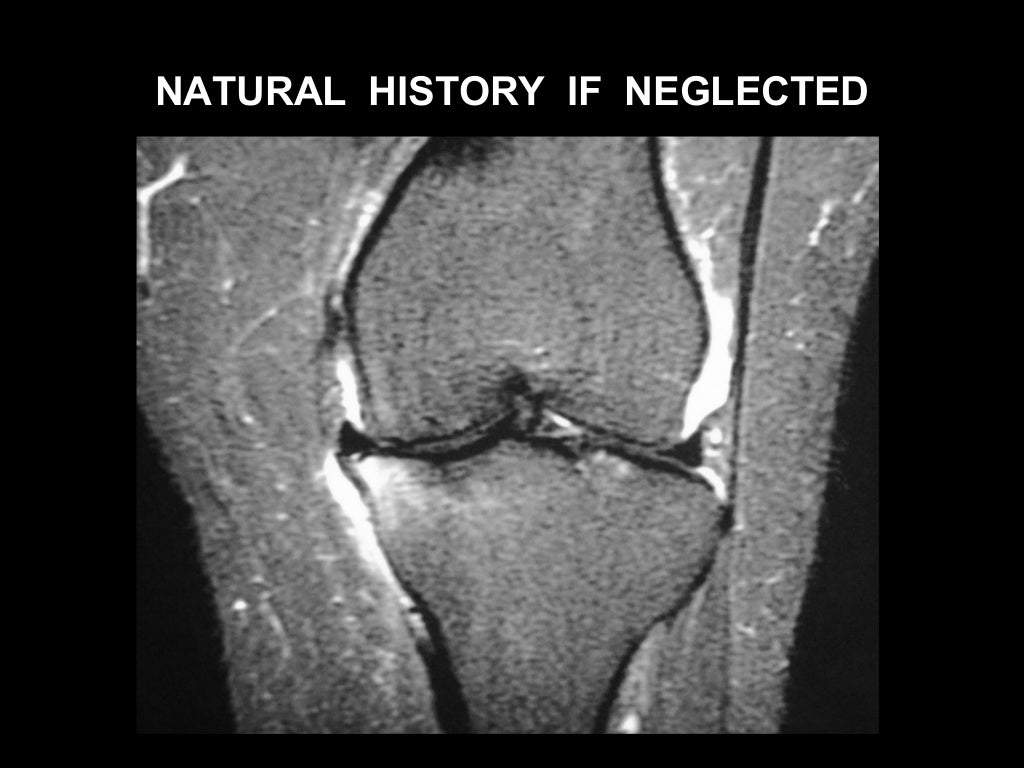
A meniscus root tear can totally destabilize the shock absorbing function of the meniscus and can lead to insufficiency fractures, spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee (SONK) and early onset arthritis in patients.
Is meniscus root repair successful?
The general published success rate for a meniscus root repair is between 80% and 85%.
Can you walk with a torn meniscus root?
With arthroscopic surgical meniscal root repair the patient can expect the use of crutches for 1-2 weeks as well as physical therapy. Total recovery time is approximately 3 months.
How long does it take to recover from meniscus root repair?
Squatting, lifting from a squat and sitting cross-legged should be avoided for 3-4 months. Stationary biking is allowed after 6-weeks with Dr. Nwachukwu's approval and assessment of healing. Full recovery usually takes 6 months but can take up to 1 year.
How long does a meniscus root repair take to heal?
Procedure for Meniscus Root Repair Suturing or repairing the meniscus root will need a period of 4 to 6 weeks of crutch use as well as physical therapy.
What does a meniscus root tear feel like?
Causes of Meniscus Root Tears and the patient may feel a “pop” in the back of their knee. Also, in most patients, they have pain in the back, or to the inside, aspect of their knee due to the meniscus basically being squished out of the knee because it is no longer attached to bone (we call this “extrusion”).
How do I know if my meniscus root repair failed?
Failed Meniscus RepairPatients older than 40 years of age.Delayed treatment.Ragged, degenerative and complex tears.Full-thickness tear.Tears in the inner margin that lack blood supply.
What is a meniscal root tear?
There are two types of meniscal root tears. The first is a traumatic tear that typically occurs in younger patients in association with a knee ligament injury. The second is a degenerative tear resulting from a low-energy injury mechanism in older patients, such as getting up from a deep-seated position.
How to repair meniscus posterior horn root?
Our preferred technique for meniscus posterior horn root repair uses a suture-passing device to create locking loop stitches, which are passed through the tibia, tensioned and fixed on the anterior cortex. This method is safe, efficient and reproducible and creates a biomechanically strong repair without the need for a posterior portal.
How to use a cannula for meniscus tear?
A free No. 0 non-absorbable suture is then passed through the torn meniscus in a locking loop configuration using a self-retrieving suture passing device (NovoStitch; Ceterix Orthopaedics or the Knee Scorpion, Arthrex) (Figure 5). Locking loop sutures are placed (Figure 6) along with a simple “leader” stitch close to the socket. This stitch will lead the meniscus tissue into the socket during tensioning. The sutures should then be individually tightened to remove slack. Next, all sutures are shuttled through the tibial socket using the previously placed passing suture. The knee is cycled to remove the creep from the repair construct.
What is the procedure for meniscus posterior horn root repair?
The direct fixation procedure is technically demanding because the sutures are inserted through a posterior portal with a curved suture-shuttling device that may be difficult to manipulate in the knee joint. A recent study evaluating the strengths of various suture techniques found a locking loop provides significantly higher load-to-failure than other suture configurations.
What is degenerative tear?
The degenerative tears are usually full-thickness radial tears near the root junction, but not a true avulsion of the meniscal attachment to bone (Figure 2). These tears can be associated with early knee arthritis. Indications for repair in this setting are evolving and the optimal candidate has not yet been defined.
How to perform a reverse notchplasty?
In addition, a reverse notchplasty may be performed by removing a small amount of bone from the wall of the notch and shaving down the medial tibial spine.
How long after knee surgery can you use a brace?
During the first 4 weeks after surgery, full extension toe-touch weight-bearing in a brace and knee flexion to 90° are allowed. After 4 weeks, the brace is discontinued and the patient may begin full weight-bearing and full knee range of motion as tolerated.
How to tell if a meniscus is torn?
A torn meniscus often can be identified during a physical exam. Your doctor might move your knee and leg into different positions, watch you walk and ask you to squat to help pinpoint the cause of your signs and symptoms.
What is the best way to detect a torn meniscus?
MRI. This uses radio waves and a strong magnetic field to produce detailed images of both hard and soft tissues within your knee. It's the best imaging study to detect a torn meniscus.
What to do after meniscus surgery?
After surgery, you will need to do exercises to increase and maintain knee strength and stability. If you have advanced, degenerative arthritis, your doctor might recommend a knee replacement.
How does a knee splint work?
The device contains a light and a small camera, which transmits an enlarged image of the inside of your knee onto a monitor. If necessary, surgical instruments can be inserted through the arthroscope or through additional small incisions in your knee to trim or repair the tear.
How to help knee pain?
Ice can reduce knee pain and swelling. Use a cold pack, a bag of frozen vegetables or a towel filled with ice cubes for about 15 minutes at a time, keeping your knee elevated .
How to strengthen knees?
Physical therapy can help you strengthen the muscles around your knee and in your legs to help stabilize and support the knee joint.
Can you have a knee replacement if you have arthritis?
If you have advanced, degenerative arthritis, your doctor might recommend a knee replacement. For younger people who have signs and symptoms after surgery but no advanced arthritis, a meniscus transplant might be appropriate. The surgery involves transplanting a meniscus from a cadaver.
How to repair a meniscus root?
Repairs are performed via arthroscopy (keyhole surgery). Repair of the meniscus root involves passing stitches into the meniscus remnant, and re-anchoring it to the bone.
What is the treatment for meniscus root tears?
Patients who are unsuitable for repair are generally treated non-surgically, with tablets and perhaps an injection of corticosteroid to minimise pain. If this is insufficient, surgical procedures such as unicompartmental knee replacement or high tibial osteotomy are very successful in removing the pain. Meniscus root tears – a devastating injury ...
What happens when a meniscus tear is extruded?
Once the meniscus is pushed out, or extruded, the underlying cartilage can start to rapidly deteriorate. The bone nearby can frequently become inflamed, causing significant pain. Studies have shown that the majority of patients ...
How long does it take for a medial meniscus root to heal?
Studies have shown that the majority of patients who suffer medial meniscus root tears which cannot be repaired undergo a rapid progression of arthritis in that region and progress to knee replacement within 5 years, and many within 1 year. Excellent results have been obtained with surgical repair of the meniscus root.
Why do meniscus tears occur?
They can occur in younger patients as a result of high energy trauma, but are more common in patients between 45 and 60 as a result of degeneration of the meniscus with age.
What is the function of the meniscus?
The meniscus of the knee performs a very important function and protects the underlying cartilage. The articular cartilage of the knee is the smooth running surface of the joint, and is made of a substance called hyaline cartilage. There are two menisci in each knee, and they are made of a soft rubbery material called fibrocartilage.
How many menisci are there in each knee?
There are two menisci in each knee, and they are made of a soft rubbery material called fibrocartilage. Each meniscus is C-shaped, and attached only to the bone of the tibia by the meniscus roots. The roots and the outer rim of the meniscus prevent the meniscus from being pushed sideways out of the joint when the knee bears load. ...
Meniscus Root Repair Rehab & Recovery
On Wednesday, February 20, 2019, I had a meniscus root repair surgery on my left knee. My MRI showed an extensive radial tear adjacent to the medial meniscus root insertion, as well as evidence of high-grade chondral loss involving the central trochlea.
The Injury: What came first, the Brazilian Jiu Jitsu or my awesome dancing at a wedding?
I don’t remember how or when I tore my meniscus. I started Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu about four years ago. The left knee was feeling great up until about a year and a half ago, when I started noticing some pain.
My Rehab
I opened my gym shortly after taking up strength training in earnest to help address my back pain, and have been working for the past eight years to help others embrace their true potential and strength. Had I not been training all these years, I would not have had the slightest idea of how to rehab my knee after surgery.
Wrap Up
As of August 20, 2019, it will be six months post-op. I plan to squat 135 pounds for three sets of five on this day and am scheduled to deadlift 200 pounds on August 23. And unless you have been following my Instagram page and know about my rehab, you would never even know that I had knee surgery.
Why are meniscal root tears so hard to treat?
This is because they are not commonly diagnosed until the progression of arthritis is more severe.
Where is the meniscus root located?
The meniscus root is where the main body of the meniscus attaches to the bone. There are meniscal root attachments both in the front and back of the tibia.
Why are root attachments important?
These root attachments are important because they hold the meniscus in place, provides stability to the circumferential hoop fibers of the meniscus, and prevents meniscal extrusion. When there is a tear of the meniscal root, it has been demonstrated on biomechanical testing that it is equivalent to having the whole meniscus removed.
What is radial root tear?
These are called radial root tears and are about 90% of all meniscal root tears. A meniscus root tear can totally destabilize the shock absorbing function of the meniscus and can lead to insufficiency fractures, spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee (SONK) and early onset arthritis in patients.
Can meniscus tears cause knee pain?
It is not uncommon for patients who are in their 50s or 60s with meniscus root tears to also have concurrent patellofemoral chondromalacia (a kind term for arthritis). Thus it is important to differentiate the location of the pain in the knee to determine if it is coming from a potential meniscus root tear or from the patellofemoral arthritis. Usually, patients with pain in their kneecap joint have pain with squatting and lunges right on the front of their knee, whereas patients with meniscal root tears usually have pain in the very back of the knee, especially with deep squatting activities. In addition, patients can have the meniscus slip out of the joint, called extrusion. This can also sometimes be quite painful and can help to differentiate between patients who may have some preexisting patellofemoral arthritis (kneecap arthritis) and those that may have a meniscus root tear.
Can a meniscal root tear be severe?
The consequences of a meniscal root tear appear to be much more severe in this age group. A meniscal root tear, which can occur with minor or seemingly trivial trauma, with a pop in the back of their knee with deep flexion, squatting and lifting, and other activities, can be quite severe. It is in this group of patients for which ...
Can a partial root tear be trimmed?
Our classification has called a partial root tear as a type 1 tear, and these can usually be trimmed without any significant consequence to the knee. Complete radial tears, which are type 2 tears, always should be considered for repair in patients who may need them, to prevent the development of osteoarthritis.
Why repair meniscal root?
Due to the dissatisfaction with partial meniscectomy in the treatment of meniscal root tears in the athlete, there has been a growing interest in meniscal repair (5,6), and this has led to a number of different types of repairs with different fixation methods. In the athletic population, repair of meniscal root injuries is indicated for both symptomatic relief and prevention of degenerative joint disease. The main indications for meniscal repair include (7,8):
What is Chris Mallac's article about meniscal root tears?
In part one of this two-part article, Chris Mallac explored the anatomy, diagnosis and imaging options for meniscal root tears. In this article, he discusses the management options for meniscal root tear injuries.
What is medial root tear?
An acute medial root tear is often associated with a multiligamentous knee injury, specifically a complete tear of the MCL where the meniscocapsular ligaments are maintained but the meniscus is avulsed at the root (9) . In these situations, there is a clear indication for a root repair to prevent the development of arthritis.
When to avoid knee flexion?
It is important to avoid any active knee flexion ranging in the first six weeks to avoid the hamstring and popliteus pulling on the meniscus (due to their attachment onto the meniscus).
What is traumatic root tear?
Acute, traumatic root tears in patients who have yet to develop osteoarthritis, with the goal of preventing arthritic changes in the future; Chronic symptomatic root tears in young or middle-aged athletes without significant pre-existing arthritis.
Is pull out repair better than meniscectomy?
Lee et al concluded that for the treatment of medial meniscus root tears, the arthroscopic pull-out repair provides better clinical and radiographic outcomes in the long-term than partial meniscectomy (2). It also has a higher potential to completely heal the meniscus that facilitates the ability of the meniscus to convert axial load into hoop stress.
Is meniscectomy recommended for athletics?
In the athletic population, partial or complete meniscectomy is not recommended as it only provides short term relief of symptoms and the long-term outcomes are not known. To summarise a few studies that have compared meniscectomy versus repair:
How to repair meniscus root?
This technique allows for anatomic reduction and fixation of the meniscal root by restoring the joint contact pressure and area similar to the intact state. Of note, drilling tibial tunnels may improve healing of the meniscus-bone interface due to the presence of progenitor cells and growth factors derived from the bone marrow. Chronic tears may be scarred to the capsule and require release of the meniscocapsular junction to allow anatomic repair.
What is medial meniscus root tear?
Medial meniscal root tears are “radial” tears within 1 cm of the meniscal root insertion or an avulsion of the insertion of the meniscus. These injuries have been reported to change joint loading due to failure of the meniscus to convert axial loads into hoop stresses. This leads to decreased contact area and increased contact pressure and ultimately results in joint overloading and degenerative changes in the knee similar to a total meniscectomy state. This tear pattern was historically unrecognized, although more recently it has been suggested this “hidden” pathology may account for nearly 80% of the total knee replacements in patients younger than 60 years. Biomechanical studies have demonstrated that repair of medial meniscus posterior root tears leads to improved contact mechanics. Studies have also reported that patients who underwent a repair of the posterior root in the medial meniscus slowed the progression of arthritic changes compared with those who had a meniscectomy; although, this did not completely prevent the arthritic changes.
What ligament prevents anterior translation of the knee?
Recent kinematic/biomechanical studies have also shown the importance of the medial meniscus to anterior translation of the knee. Absence of the medial meniscus (entire medial meniscal root tear) places large stresses on the ACL, the primary ligament that prevents anterior translation of the knee.
Why is it so hard to diagnose a medial meniscal root tear?
Making a medial meniscal root tear diagnosis is difficult because the typical history of locking, catching or giving way is less likely to be present. More often, the patient will complain of joint line pain with a minor traumatic event, such as squatting.
Why is medial meniscus tear important for ACL reconstruction?
As such, it is critical to repair medial meniscal root tears during ACL reconstruction to help stabilize the knee, as well as to decrease stresses that the graft experiences.
What is the function of the medial meniscus?
The medial meniscus transmits approximately 50% of the total joint load of the knee medial compartment, thus protecting the articular cartilage from excessive force.
What causes a knee to degenerate after a meniscectomy?
Tears to the medial meniscal root change the biomechanics and kinematics of the k nee, which cause early degeneration of the joint. It has been shown the peak tibiofemoral contact pressure after a total meniscectomy is equal to a posterior medial meniscal root tear.
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Treatment for a torn meniscus often begins conservatively, depending on the type, size and location of your tear. Tears associated with arthritis often improve over time with treatment of the arthritis, so surgery usually isn't indicated. Many other tears that aren't associated with locking or a block to knee motion will become less painful over ti...
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Avoid activities that aggravate your knee pain — especially sports that involve pivoting or twisting your knee — until the pain disappears. Ice and over-the-counter pain relievers can be helpful.
Preparing For Your Appointment
- The pain and disability associated with a torn meniscus prompt many people to seek emergency care. Others make an appointment with their family doctors. Depending upon the severity of your injury, you might be referred to a doctor specializing in sports medicine or a specialist in bone and joint surgery (orthopedic surgeon).